- Home
- Patient Care
- Services
- Pediatric and Adolescent Orthopedic Surgery
- Overview
- Pediatric Spine Patient Education Overview
- Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis
Juvenile ankylosing spondylitis (JAS) is a type of arthritis that affects the spine and sites where muscles, ligaments, and tendons are attached to the bone. “Ankylosing” means stiff or rigid, spondyl” means spine, and “itis” means inflammation. JAS causes inflammation in the spine and large joints, resulting in stiffness, pain and joint fusions. JAS affects males two to three times more often than females, and is thought to run in families.
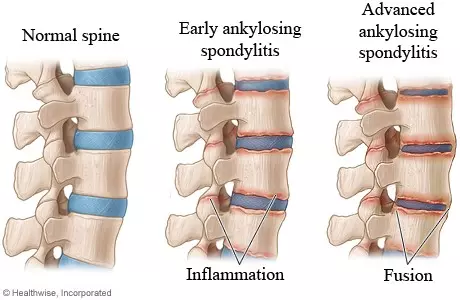
What are the symptoms of JAS?
- Back pain and sometimes stooped posture
- Early morning stiffness
- Inability to take deep breath
- Appetite loss and weight loss
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Anemia
- Joint pain, particularly in the legs
- Pain at the site of muscles, ligaments, and or tendons to bone
- Organ damage, such as heart, lungs, and eyes
- Eye pain, redness, and light sensitivity
- Vague pain, usually in buttocks, thighs, heels, or near shoulders
How is it diagnosed?
JAS is diagnosed by physical exam, history, x-rays, and blood tests. Genetics or family history are thought to play a role in the development of JAS, so family history is important to know. A specialized treatment plan will be developed based on all of the previously mentioned information. Children with JAS require care from specialists such as rheumatologists, geneticists, orthopedists, etc.
More Information