- Home
- Patient Care
- Services
- Pediatric and Adolescent Orthopedic Surgery
- Overview
- Pediatric Spine Patient Education Overview
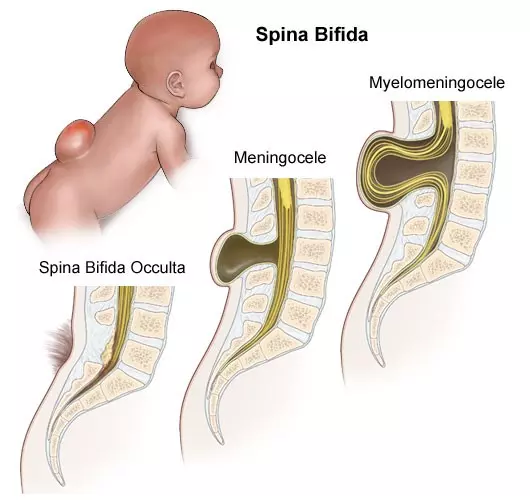
- Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is a severe form of spina bifida in which the spinal cord and nerves develop outside of the body and are contained in a fluid-filled sac that is visible outside of the back area. These babies typically have weakness and loss of sensation below the sac. This can result in muscle weakness and/or paralysis, bowel and bladder problems, excessive fluid on the brain (hydrocephalus), change in positioning of the brain (Chiari Malformation), seizures, and orthopedic conditions (scoliosis, hip problems, and foot deformities). Myelomeningocele affects about 1 in every 1,000 babies.
What causes myelomeningocele?
The exact cause is unknown, but a lack of folic acid, exposure to viruses, exposure to radiation, and/or genetics are suspected.
How is it diagnosed?
It is diagnosed with prenatal blood work, amniocentesis, physical exam, and ultrasound. An MRI is sometimes needed to get more information and guide care.
How is it treated?
Most cases of myelomeningocele are treated surgically with a repair soon after birth. In some cases, the repair is done while still in the womb prior to delivery. Children that have hydrocephalus will likely require surgery to decrease fluid on the brain (VP shunt). Children with myelomeningocele often require care from multiple specialities such as neurology, physical therapy, orthopedics, and etc.
More Information